主方法2025年3月17日 | 阅读 3 分钟 主方法用于解决以下类型的递归式 T (n) = a T + f (n) 其中 a≥1 且 b≥1 是常数,f(n) 是一个函数, + f (n) 其中 a≥1 且 b≥1 是常数,f(n) 是一个函数, 可以解释为 可以解释为 设 T (n) 在非负整数上定义,由递归式得到。 T (n) = a T + f (n) + f (n)
在递归算法的函数分析中,常量和函数具有以下意义 - n 是问题的规模。
- a 是递归中子问题的数量。
- n/b 是每个子问题的规模。(这里假设所有子问题的规模基本相同。)
- f (n) 是在递归调用之外完成的工作的总和,包括划分问题和组合子问题解的总和。
- 不可能总是根据要求限制函数,所以我们设置了三种情况,告诉我们可以在函数上应用什么样的界限。
主定理可以在这三种情况下完成渐近紧界  情况 1:如果 f (n) =  对于某个常数 ε >0,则得出 对于某个常数 ε >0,则得出 T (n) = Θ 
示例 T (n) = 8 T  apply master theorem on it. apply master theorem on it.
解决方案 Compare T (n) = 8 T  with
T (n) = a T with
T (n) = a T  a = 8, b=2, f (n) = 1000 n2, logba = log28 = 3
Put all the values in: f (n) =
a = 8, b=2, f (n) = 1000 n2, logba = log28 = 3
Put all the values in: f (n) =  1000 n2 = O (n3-ε )
If we choose ε=1, we get: 1000 n2 = O (n3-1) = O (n2)
1000 n2 = O (n3-ε )
If we choose ε=1, we get: 1000 n2 = O (n3-1) = O (n2)
由于该等式成立,主定理的第一种情况适用于给定的递归关系,从而得出结论 T (n) = Θ  Therefore: T (n) = Θ (n3)
Therefore: T (n) = Θ (n3)
情况 2:如果对于某个常数 k ≥ 0,以下成立 F (n) = Θ  then it follows that: T (n) = Θ then it follows that: T (n) = Θ 
示例 T (n) = 2 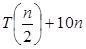 , solve the recurrence by using the master method.
As compare the given problem with T (n) = a T , solve the recurrence by using the master method.
As compare the given problem with T (n) = a T a = 2, b=2, k=0, f (n) = 10n, logba = log22 =1
Put all the values in f (n) =Θ a = 2, b=2, k=0, f (n) = 10n, logba = log22 =1
Put all the values in f (n) =Θ  , we will get
10n = Θ (n1) = Θ (n) which is true.
Therefore: T (n) = Θ , we will get
10n = Θ (n1) = Θ (n) which is true.
Therefore: T (n) = Θ  = Θ (n log n)
= Θ (n log n)
情况 3:如果 f(n) = Ω  对于某个常数 ε >0,并且也成立:a f 对于某个常数 ε >0,并且也成立:a f  对于某个常数 c<1 对于较大的 n 值,则 对于某个常数 c<1 对于较大的 n 值,则 示例: 解决递归关系 T (n) = 2 
解决方案 Compare the given problem with T (n) = a T  a= 2, b =2, f (n) = n2, logba = log22 =1
Put all the values in f (n) = Ω
a= 2, b =2, f (n) = n2, logba = log22 =1
Put all the values in f (n) = Ω  ..... (Eq. 1)
If we insert all the value in (Eq.1), we will get
n2 = Ω(n1+ε) put ε =1, then the equality will hold.
n2 = Ω(n1+1) = Ω(n2)
Now we will also check the second condition:
2 ..... (Eq. 1)
If we insert all the value in (Eq.1), we will get
n2 = Ω(n1+ε) put ε =1, then the equality will hold.
n2 = Ω(n1+1) = Ω(n2)
Now we will also check the second condition:
2  If we will choose c =1/2, it is true:
If we will choose c =1/2, it is true:
 ∀ n ≥1
So it follows: T (n) = Θ ((f (n))
T (n) = Θ(n2) ∀ n ≥1
So it follows: T (n) = Θ ((f (n))
T (n) = Θ(n2)
| 